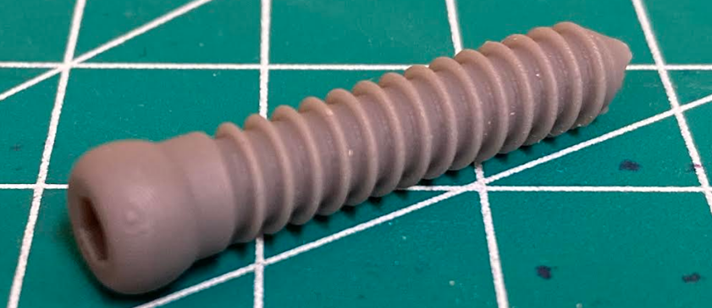
HA 6.5 Bone Screw
Project Overview
Feasibility of using polymer screw evaluated for pediatric fracture fixation. Bone screw designed and analyzed using computation and finite element analysis. Uniaxial tensile testing performed on prototype.
Project Objective
Design an Orthopedic HA 6.5 cortical screw equipped with a through hole for a Kirschner wire. Prototype with SLA Resin. Test SLA Resin printed screw using Instron uniaxial testing.
Specifications
- Design to ASTM F543 - 17
- Manufacturable from Standard Resin on a Formlabs Form 3 printer.
- Withstand uniaxial pullout force of 100 N
Technical Process
1. Design & Modeling
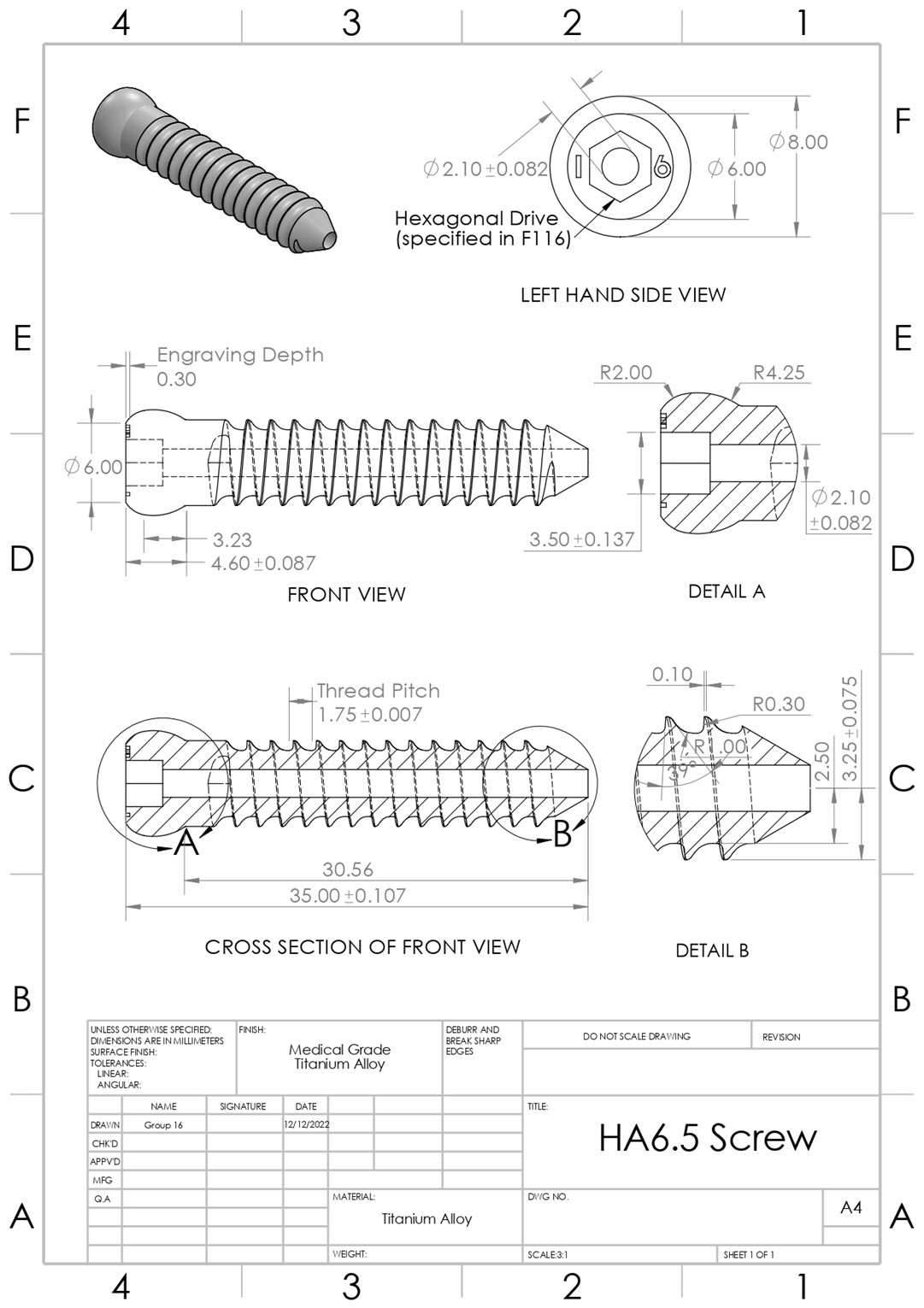
HA 6.5 orthopedic screw modeled in SolidWorks to ASTM F543-17 standards.
2. Engineering Calculations
Maximum k-wire hole diameter was calculated w/ a Factor of Safety of 3 using minimum tensile stress area calculations.
3. Finite Element Analysis
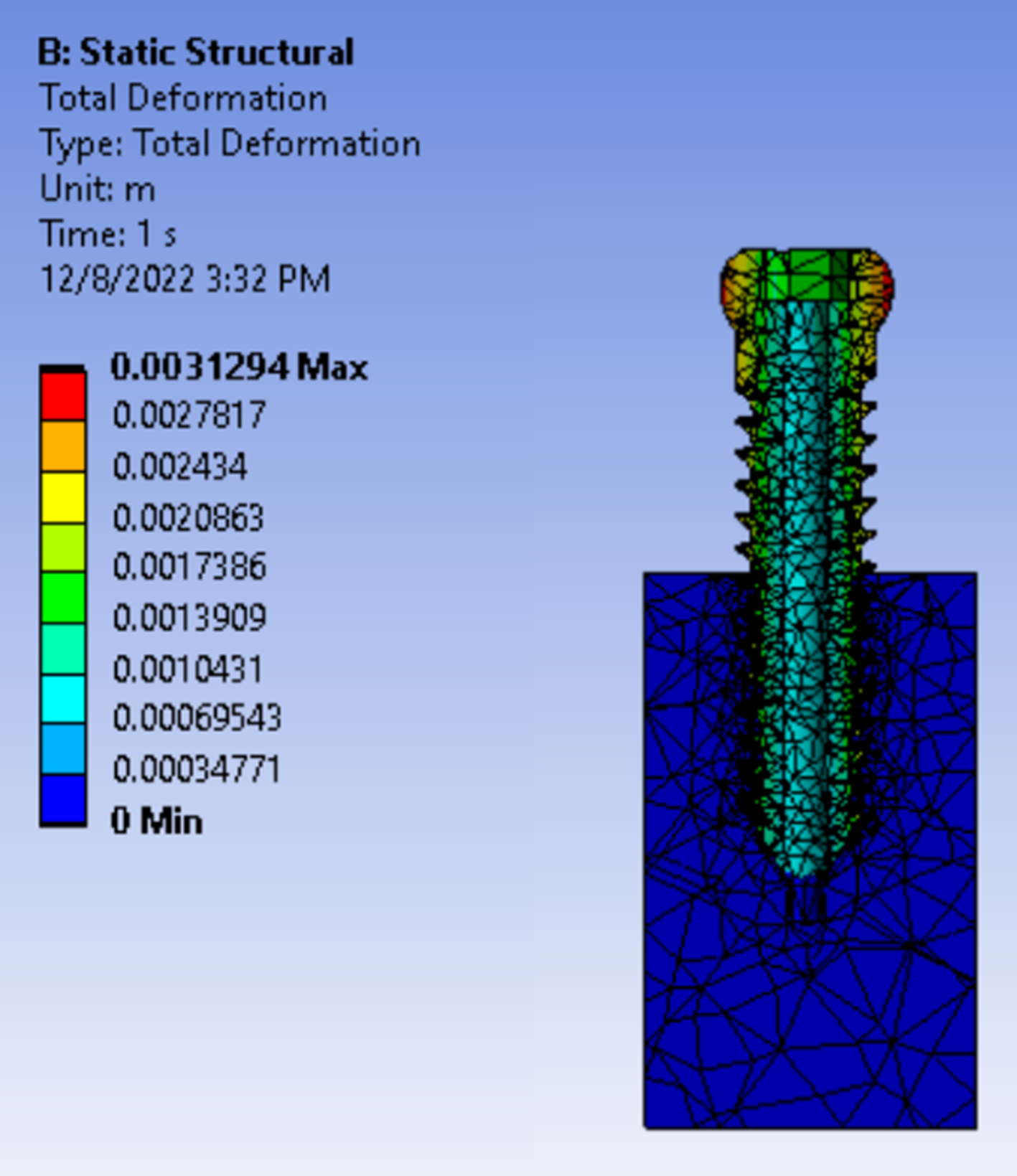
Explicit Dynamics FEA was performed in ANSYS to validate calculations, predict deformation and evaluate stress concentrations.
4. Prototyping
Screws SLA printed in Standard Resin on a Formlabs Form 3L. Design considerations included overhangs, engraving depth, and layer thickness.
5. GD&T
Performed visual inspection including grinding to centerline to view cross-section. Key dimensions were measured using digital calipers and recorded tolerances recorded.
6. Mechanical Testing
Uniaxial tensile testing was conducted on Instron per ASTM Section A3. Failure modes were visually inspected, data was compared to FEA.
Outcome and Impact
- Found that SLA printed resin screw was not suitable for pediatric fracture fixation due to insufficient thread strength.
- Reaffirmed that FEA is a reliable predictor of physical testing outcomes when executed properly.
Image Gallery